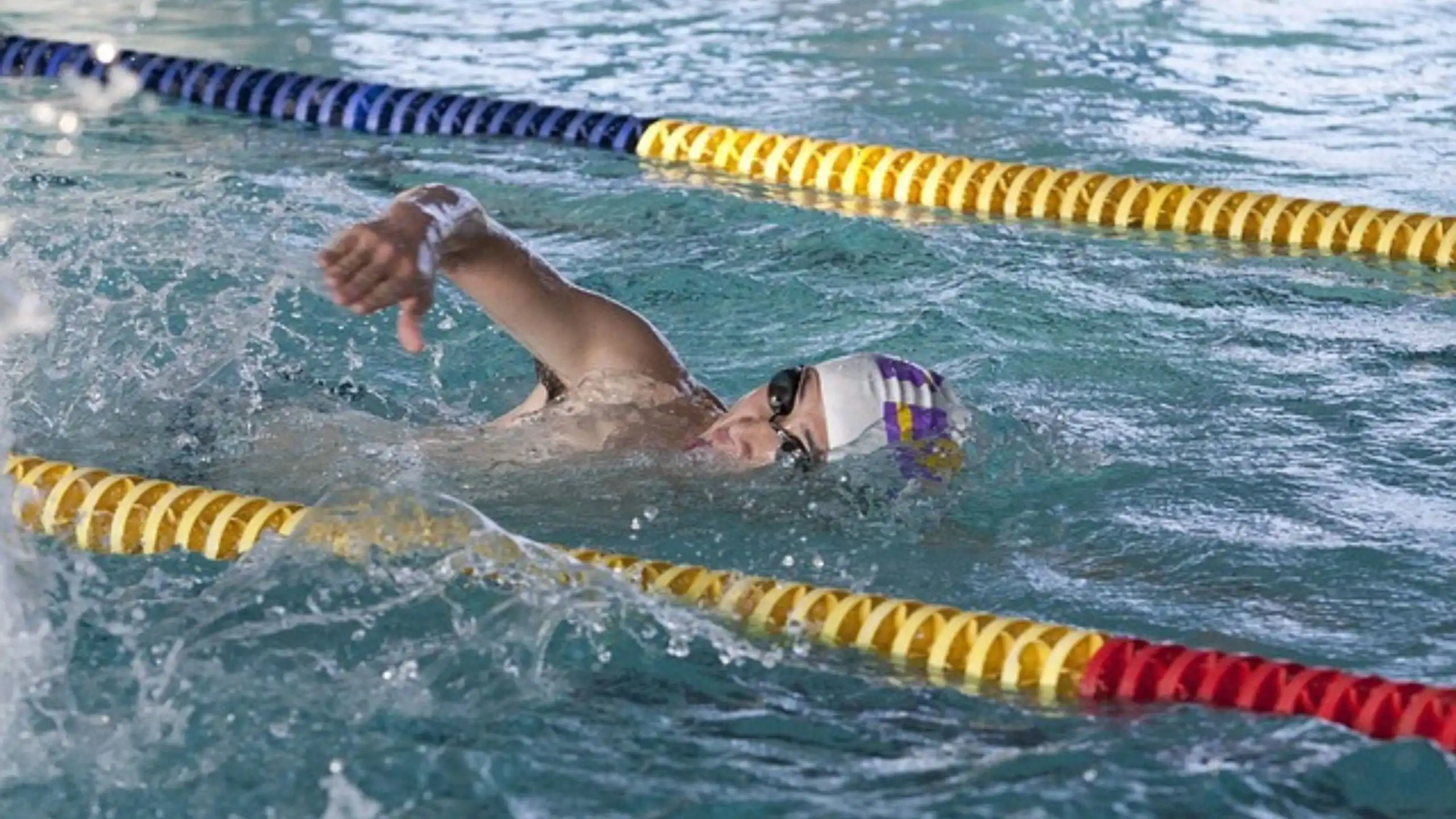
Swimming is a universally beloved activity that offers incredible health benefits, recreational enjoyment, and a competitive edge for athletes. Whether you’re dipping your toes into the water for the first time or aiming to refine your technique, swimming is a skill that opens up a world of possibilities. This article dives deep into the art of swimming, exploring its techniques, health benefits, safety tips, and much more.
In This Post
What is Swimming?
Swimming is the act of moving through water using coordinated movements of the arms, legs, and torso. This skill has been practiced for centuries for survival, leisure, and competition. As one of the most versatile physical activities, swimming caters to all ages and fitness levels.
Types of Swimming Strokes
Mastering various swimming strokes enhances efficiency, builds strength, and adds variety to your workouts. Here are the most common strokes:
Freestyle (Front Crawl)
The fastest and most efficient stroke, freestyle requires alternating arm movements with a flutter kick. It’s perfect for competitive swimming and cardio workouts.
Breaststroke
This stroke is characterized by a frog-like kick and symmetrical arm movements. While slower, it’s great for beginners due to its simplicity and focus on controlled breathing. Ranksfocus
Backstroke
Performed on your back, this stroke improves posture and strengthens upper body muscles. It’s also a relaxing stroke for swimmers who enjoy a steady pace.
Butterfly
Known for its power and grace, the butterfly stroke demands strength and coordination. It’s ideal for advanced swimmers seeking a challenge.
Sidestroke
Often used in lifesaving and recreational swimming, sidestroke involves a scissor kick and one-sided arm pull, making it a low-effort yet efficient stroke.
The Health Benefits of Swimming
Swimming provides a unique combination of physical and mental health benefits, making it a favorite among fitness enthusiasts:
Full-Body Workout
Swimming engages all major muscle groups, including the core, arms, legs, and back. This results in improved strength, flexibility, and endurance.
Cardiovascular Fitness
As a high-intensity aerobic activity, swimming enhances heart health, lowers blood pressure, and increases lung capacity.
Low-Impact Exercise
The buoyancy of water reduces stress on joints and bones, making swimming an excellent option for individuals with arthritis or injuries.
Calorie Burning
Swimming is a great calorie-burning activity. For example, a 155-pound person burns approximately 400 calories in 30 minutes of vigorous swimming.
Mental Health Boost
Swimming promotes relaxation, reduces stress, and releases endorphins. The rhythmic movement and calming water environment contribute to better mental well-being. rank post
Swimming as a Life Skill
Learning to swim is essential for safety and recreation. Here’s why:
Survival Skills: Swimming equips individuals with life-saving skills, particularly in emergency water situations.
Social Connection: Swimming pools, beaches, and clubs provide opportunities for community interaction.
Access to Activities: Knowing how to swim opens doors to sports like diving, water polo, and synchronized swimming.

Tips for Improving Swimming Technique
Enhancing your swimming technique not only improves efficiency but also makes the activity more enjoyable:
Focus on Body Position
Maintain a horizontal position in the water to minimize drag and maximize speed.
Master Breathing Techniques
Learn to exhale underwater and inhale quickly when you surface. Proper breathing improves endurance and performance.
Refine Arm Movements
Keep your arm strokes smooth and consistent. Focus on pulling water effectively to propel yourself forward.
Strengthen Your Kick
A steady and controlled kick adds power to your swim without wasting energy. Practice with a kickboard to build strength.
Use Swim Aids
Incorporate equipment like fins, pull buoys, and paddles to target specific muscle groups and refine technique.
Safety Tips for Swimming
Swimming safety is paramount, whether you’re in a pool or open water. Follow these guidelines to ensure a safe experience:
Supervise Children
Always keep an eye on children near water. Use floatation devices if necessary.
Learn CPR
Knowing CPR can save lives during emergencies, especially in water-related incidents.
Follow Pool Rules
Obey posted rules, including diving restrictions and lane etiquette.
Stay Hydrated
Swimming can dehydrate you quickly. Drink water before and after your swim to stay refreshed.
Respect Nature
When swimming in lakes, rivers, or oceans, be aware of currents, tides, and marine life. Wear reef-safe sunscreen to protect aquatic ecosystems.

Competitive Swimming
For those who aspire to take swimming to the next level, competitive swimming offers exciting opportunities:
Training Routines
Competitive swimmers combine intensive pool workouts with strength training, flexibility exercises, and mental preparation.
Swim Meets
Events include individual races, relay teams, and open water competitions. Each test has skill, speed, and endurance.
Benefits of Competition
Competing enhances discipline, goal-setting, and teamwork while fostering a sense of accomplishment. solar gadget
Swimming for Recreation and Fitness
Not everyone swims for medals—many enjoy it for relaxation and fitness:
- Family Fun: Swimming is a popular activity for families, providing entertainment and exercise.
- Stress Relief: The calming nature of water and rhythmic movements reduce tension.
- Fitness Maintenance: Regular swimming keeps you fit without the harsh impact of other workouts.
Swimming for Rehabilitation
Swimming and water therapy are effective for rehabilitation. They help patients recovering from injuries, surgeries, or chronic conditions regain mobility and strength without overloading joints.
Eco-Friendly Swimming Practices
As swimming enthusiasts, we can help preserve the environment by:
- Supporting sustainable swimming pools with eco-friendly heating and filtration systems.
- Avoiding littering in natural water bodies.
- Choosing biodegradable or reef-safe sunscreens.
Conclusion
Swimming is a timeless activity that enriches lives with its myriad of benefits. Whether you’re diving in for fitness, recreation, or competition, this low-impact, high-reward sport offers something for everyone. By mastering techniques, prioritizing safety, and embracing the joy of water, you can make swimming an integral part of your lifestyle.
(FAQs) About Swimming
Why is swimming considered a great workout?
Swimming is a full-body workout that engages multiple muscle groups, improves cardiovascular fitness, and is easy on the joints due to water buoyancy. It’s suitable for all fitness levels.
How often should I swim to see health benefits?
Swimming 2–3 times a week for at least 30 minutes per session can yield significant improvements in strength, endurance, and mental well-being.
What are the best swimming strokes for beginners?
The freestyle (front crawl) and breaststroke are beginner-friendly because they allow for straightforward movements and easy breathing patterns.
Is swimming effective for weight loss?
Yes, swimming is an excellent calorie-burning exercise. Depending on intensity and body weight, you can burn between 200 to 500 calories per half-hour of swimming.
Can swimming improve posture?
Absolutely. Strokes like backstroke and freestyle strengthen core and back muscles, helping to correct posture and alleviate back pain.
Do I need the equipment to start swimming?
While swimming doesn’t require much equipment, essentials include a swimsuit, goggles, and a swim cap. For beginners, kickboards and pull buoys can help improve technique.
How can I overcome a fear of water?
Start by familiarizing yourself with water in a shallow, calm environment. Consider taking swimming lessons with a certified instructor to build confidence gradually.
What are the key safety tips for swimming?
Always swim in designated areas with lifeguards, never swim alone, and ensure children are supervised at all times. Learning basic water safety and CPR is highly recommended.
Can swimming help with recovery from injuries?
Yes, swimming is a low-impact activity often used in rehabilitation programs. It helps improve mobility, strength, and endurance without putting stress on joints.
How can I improve my swimming technique?
Focus on body alignment, controlled breathing, and efficient arm and leg movements. Practicing consistently and using training aids like fins can also enhance your technique.
Is swimming safe during pregnancy?
Swimming is generally safe and beneficial during pregnancy as it relieves joint pressure, reduces swelling, and provides a gentle form of exercise. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting.
What are the environmental considerations for swimmers?
Use eco-friendly sunscreens, avoid polluting water bodies, and support swimming facilities that use sustainable practices like efficient heating and filtration systems.
How can I prevent swimmer’s ear?
Dry your ears thoroughly after swimming, use earplugs, and avoid swimming in water that may be contaminated to reduce the risk of ear infections.
Is open-water swimming different from pool swimming?
Yes, open-water swimming involves factors like currents, waves, and temperature changes, making it more challenging. It requires additional safety precautions and skills.
What should I eat before swimming?
Consume a light, balanced meal with carbs and proteins about 1–2 hours before swimming. Avoid heavy or fatty foods that can cause discomfort in the water.
How young can children start swimming lessons?
Children can begin learning water safety and basic skills as early as 6 months old in parent-and-child classes. Structured swimming lessons typically start around age 4.
Do I need to warm up before swimming?
Yes, performing light stretches or dynamic movements before swimming can help prevent muscle strain and improve flexibility in the water.
What’s the best way to track progress in swimming?
Use a waterproof fitness tracker or log your swim times, distances, and strokes manually. Tracking improvements in endurance, speed, and technique will motivate consistent progress.
